CRM vs. ERP – What is the difference?
Common background
The idea and concept behind CRM dates back to the 1970s, where the technology at that time limited companies to independent mainframe systems to automate sales, and eventually to categorize customers in spreadsheets.
The history of the two systems is very similar to each other
The term 'ERP' was first used in the 90's, but the system has roots back to the MRP (Material Requirements Planning) system that was developed in the 70's.
The introduction of the personal computer (PC) and client/server architecture for companies led to a boom in the development of software for managing and controlling the company's daily operations and the launch of first management system for handling contacts was born.
The two systems separated in particular during the mid-90s, when companies began to prioritize their investments in software tailored to their specific needs, such as product planning, production, shipping, marketing, customer service and payment processing.
What is a CRM system?
A CRM system is used to record and store all information related to the company's customer interactions.
CRM is customer oriented and helps to streamline your marketing activities
CRM systems, such as Microsoft Dynamics CRM, provide a standardized system that can collect and share customer data and catalog customer interactions. The standardized data is shared across the company, creating an important view of customer relationships, which can be used, for example, by management to develop sales forecasts or sales representatives who are better able to maintain close contact with the customers. In short, CRM is used to deliver a comprehensive inventory of customer data, which ultimately will help increase sales, improve customer loyalty and generally improve and streamline the company's relationship with its customers.
CRM is typically used by sales and marketing staff for the following tasks:
- Automation of business marketing processes, such as email or online advertising campaigns
- Identification of business opportunities and new potential sales leads
- Observe the customers and their buying behavior
- Managing accounts and campaigns on social media
- Organize a better support for existing customers
- Streamline the sales process and reduce the amount of repetitive work
Benefits of CRM
The CRM system stores information about the company's customers and their interaction behavior patterns. This information, or data, is collected and shared and used across the company, which, for some companies, is indispensable knowledge in terms of providing an overview of the customers and their activities. In short, the aim is to gather a comprehensive amount of detailed data about the customers and their behavior and thus improve the company's ability to launch successful marketing activities for one or more differentiated segments, which ultimately aims to increase the companys sales as much as possible, improve customer loyalty and conduct marketing activities in the most economically and efficient manner.
What is a ERP system?
Rather than, as is the case with a CRM system, focusing exclusively on the customer, the ERP system focuses on the entire company and to improve and streamline its processes. In short, CRM is customer-oriented whereas ERP is business oriented.
The ERP system is holistic and focuses on all business processes
However, what the two systems have in common is that they both allow you to quickly share standardized information across the company's departments, allowing both management and employees to enter information into the system, creating an updated and comprehensive overview of the company. That way each individual department across the company can at an early stage observe a problem in another department and plan ahead of it before it becomes a problem in their own department. In other words, an ERP system visualize the data of the entire company and is an efficient method for streamlining business processes for all company departments and units.
In short, an ERP system is typically a heavy and comprehensive system that helps to manage all aspects of the operation of a company.
- Accounting and Finance
- Service and management of customer relations
- Sales and Marketing
- Product and purchase planning
- Inventory management
- Management of fixed assets
- Project management
- Logistics
- Staff
- Production and delivery planning
- Shipping and Payment
- Supply chain management
A typical ERP system can either be delivered on-premise, such as Dynamics NAV, where you pay for the solution and host it on either your own or a provider's server, or as a subscription solution, such as Microsofts recently launched cloud ERP solution, Business Central, where you, for example, pay a monthly fee per. user.
Advantages of ERP
ERP is an invaluable tool for optimizing and streamlining the company's many complex business processes. This is especially true for large and complex companies or for small and medium-sized companies in growth. With an ERP system, the company's data becomes consolidated, manageable and accessible to relevant key features across the company, from the supply chain to the warehouse and then further from distribution to order completion and finally for accounting and finance.
A fully integrated ERP system can therefore provide updated information to all affected parts of the company in real time. For most business executives such information is essential and an ERP system is therefore indispensable. Additionally, if you integrate a BI (Business Intelligence) solution, such as Power BI, the often extensive amount of data is even more clearly presented, making it easier and faster to make decisions based on the data presented.
It can be a huge benefit to complement the ERP system with a BI solution
The differences between ERP and CRM
Despite the differences, the purpose of the two systems is ultimately the same, optimizing and thereby streamline the business processes and thereby increase profits. The purpose of the two solutions is thus the same, but it's the methods to increase profitability which separates them.
The ERP system aims to reduce the company's overall costs by streamlining workflows and business processes, thus reducing the amount of resources used to run a company.
The CRM system, on the other hand, aims to increase profits by increasing the company's sales volume. An extensive layer of customer data makes it easier for employees, ranging from managers to salesmen, to improve relationships with customers, resulting in increased brand loyalty and therefore ultimately profits.
ERP vs. CRM: Which system should you choose?
As is always the case with business systems, such a choice depends on the needs of each company, but generally an ERP system typically contains much of the functionality of a CRM system, but not vice versa.
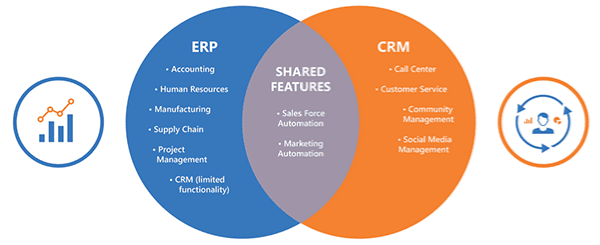 |
Despite the differences, a large part of the functionality of the two systems overlap each other
However, the functionality in the CRM system for optimizing customer experience and loyalty to the company will still be relevant for both larger and smaller companies for whom customer management is an essential part of the business and the service level is therefore a significant competitive parameter.
